Plan release information
The Cockburn groundwater allocation plan was released in January 2021. Supporting documents for the plan are also available:
- Cockburn groundwater allocation plan: Statement of response
- Cockburn groundwater allocation plan: Methods report
The statement of response summarises our response to public submissions received on the Cockburn groundwater allocation plan: for public comment, released in 2018.
The plan details our approach to regulating and managing the take of groundwater in this area.
This plan:
- accounts for the declining rainfall trend in the South West of Western Australia and the effect this will continue to have on local water availability and water quality
- confirms allocation limits set under the previous plan cannot be sustained under the drying climate to 2030
- identifies groundwater resources are now fully or over-allocated and sets out new allocation limits
- supports implementation of the Western Trade Coast heavy industry local water supply strategy 2016
- supports the use of new and existing alternative water sources to meet future demand, such as reuse of treated wastewater or managed aquifer recharge, by industry and the Water Corporation.
The plan does not:
- address access to, or use of, public potable (drinking water) and non-potable (wastewater) supply in the cities of Cockburn, Kwinana, Rockingham and surrounding areas
- replace allocation limits set in 2007 for the Leederville and Yarragadee aquifers.
Water allocation planning in the Cockburn area
Planning is essential to make sure that our water supplies are secure for future generations and the needs of the community and the environment are protected.
For the Cockburn groundwater area water management plan: Evaluation statement 2012-2015, we used groundwater monitoring, metering and modelling data to evaluate the resource. This work showed that groundwater abstraction (23 gigalitres per year out of 29.9 GL licensed in the Superficial aquifer) was likely at its limit.
The department's formal planning process to replace the 2007 Cockburn groundwater area water management plan, began in 2015, following release of the 2012–2015 evaluation statement. The review of water supply and demand for the Western Trade Coast industrial precinct, as part of the Western Trade Coast heavy industry local water supply strategy 2016, informed how we developed the plan.
The plan is necessary to provide a framework for managing groundwater use in this area for the benefit of all water users and the community. This plan provides an updated management approach to:
- account for the continuing effects of the drying climate on groundwater availability.
- minimise the effects of groundwater abstraction on environmental assets under the drying climate.
- minimise artificial movement of the seawater interface further inland.
The department will manage groundwater resources through the allocation limits, local licensing policies and monitoring program established in this allocation plan.
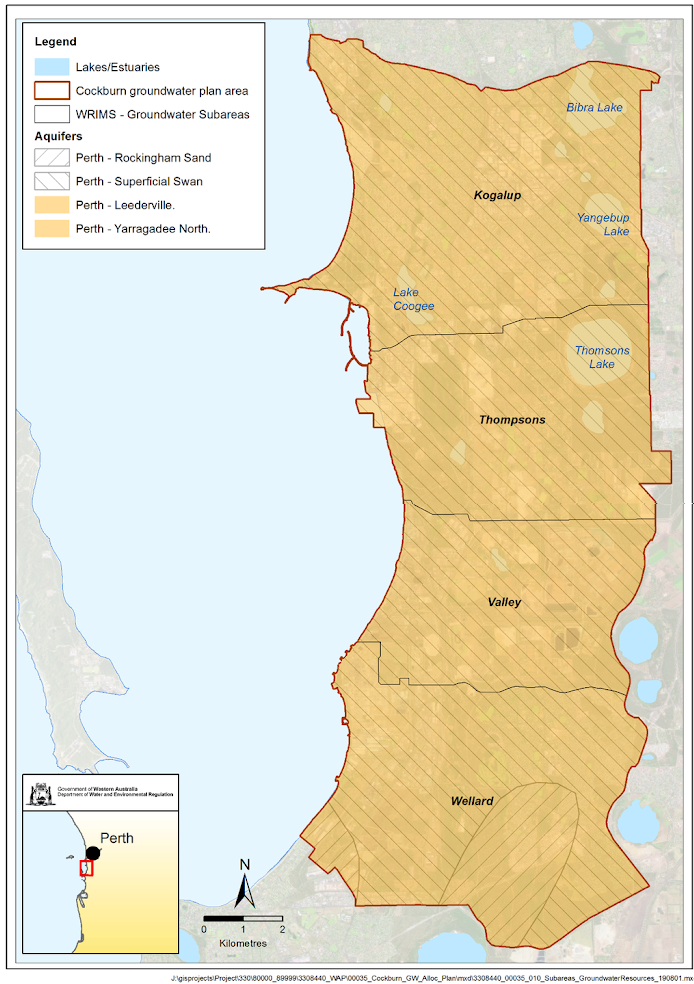
Plan area
The Cockburn plan area covers an area of 157 km2 and extends along the Swan Coastal Plain from Kwinana Beach northward 22 km to South Beach and 7 km inland. It covers the local government areas of Cockburn, Kwinana and a small part of Rockingham.
Groundwater use in this plan area is mainly for:
- Industry (Kwinana Industrial Area, Australian Marine Complex, Rockingham Industry Zone and Latitude 32 industry zone, collectively known as the Western Trade Coast industrial precinct).
- irrigation of public open space (City of Cockburn and Kwinana) and sporting grounds.
- some small-scale irrigated market gardens and turf production.
- domestic gardens.
The Ramsar-listed Thomsons Lake and parts of the Beeliar Regional Park are important key groundwater-dependent environmental features of the area.
The 2021 Cockburn groundwater allocation plan guides our management of groundwater resources to support both water users and the ecosystems that depend on groundwater.
Water resources
Groundwater in the plan area is abstracted from three aquifers: the Superficial (water-table aquifer), the underlying Leederville aquifer, and the deeper Yarragadee aquifer. It is divided into four subareas for allocation planning and licensing purposes. A ‘resource’ is the portion of an aquifer that exists in a subarea. We set allocation limits for each resource.
From north to south, the four subareas of the Cockburn plan area are:
- Kogalup
- Thompsons
- Valley
- Wellard
Publications
Cockburn groundwater allocation plan
Cockburn groundwater allocation plan: Statement of response
Cockburn groundwater allocation plan: Methods report
Cockburn groundwater allocation plan: for public comment
Cockburn groundwater area water management plan: Evaluation statement 2012-2015