The department recognises and acknowledges the Traditional Owners and custodians of the Exmouth Gulf and its surrounds, the Baiyungu, Yinikurtira and Thalanyji people. We recognise their deep and continuing connection to the land and waters of this region, and we pay respect to Elders past, present and emerging.
Plan release information
The Exmouth groundwater subarea allocation plan was released in 1999 by the former Water and Rivers Commission. The plan outlines water allocation limits (how much water can be taken out of a resource for use), local water licensing policies, and monitoring programs that will apply in the plan area.
The Exmouth groundwater subareas allocation limits review report, released in 2025 by the Department of Water and Environmental Regulation, updated water allocation limits and licensing guidance.
The two documents should be read alongside each other to obtain all the information about managing groundwater in the Exmouth plan area.
Water allocation planning in the Exmouth subareas
The plan area and groundwater resources in the Exmouth subareas are detailed below. Allocation limits manage water abstraction at a subarea or resource scale, while water licensing and monitoring requirements manage abstraction at a local scale.
We set allocation limits to manage how much water can be sustainably taken. This is influenced by the amount of groundwater needed to support water-dependent values.
In 2023–24, we reviewed the groundwater allocation limits for resources across the Exmouth Peninsula. The Exmouth groundwater subareas allocation limits review report details how we undertook the review and the resulting allocation limits and new licensing guidelines. The report includes new hydrogeological insights and details how we have accounted for the impacts of a changing climate.
The review is informing Water Corporation’s water source planning to meet existing and future demand for the Exmouth Town Water Supply Scheme while protecting important groundwater-dependent values for ongoing sustainable management.
The review report is accompanied by a report titled, The importance of water to the Exmouth Peninsula’s environmental, heritage and social values. The values report highlights groundwater-dependent ecosystems of the Exmouth Peninsula, including Cape Range Subterranean Waterways and culturally significant sites like Qualing Pool and Cameron’s Cave.
The review and values reports support the department’s advice to the Minister for Environment’s Exmouth Gulf Taskforce, including assisting Taskforce considerations of recommended options to deliver a high level of protection for the Cape Range Subterranean Waterways. Protection of the Cape Range Subterranean Waterways, and the groundwater-dependent ecological, cultural and social values, is a key interest of the taskforce and Traditional Owners.
Plan area
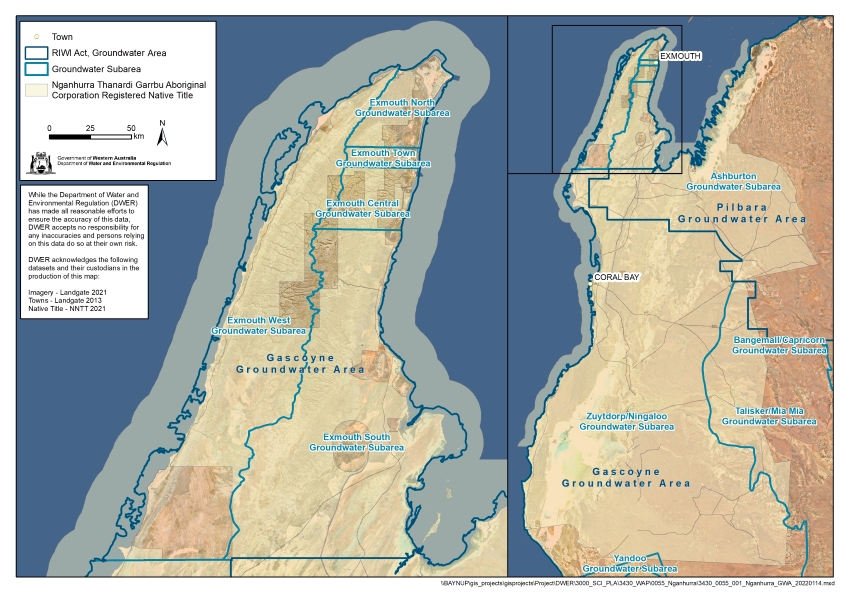
The Exmouth plan area is about 1,260 kilometres north of Perth covers 2,020 km2 of the North West Cape, on the western side of the Exmouth Gulf (see map below). It includes the Cape Range National Park, which is part of the Ningaloo Coast World Heritage Area.
The climate of the Exmouth Peninsula is semi-arid, with hot summers and milder winters. Rainfall in Exmouth has a high natural variability, both monthly and year-to-year. The big rain events are brought both by tropical cyclones from the north and low-pressure systems extending from the south between January and July. The infrequent nature of these events means that there may be several consecutive years where rainfall is low.
For management purposes, the area is divided into six groundwater subareas in the proclaimed Gascoyne Groundwater Area (see map). Following the 2024 review, the previous Exmouth South subarea (defined in the 1999 plan) was split to make two new subareas.
- Exmouth North
- Exmouth Town
- Exmouth Central
- Exmouth West
- Badjirrajirra (previously part of Exmouth South)
- Exmouth Saltflats (previously part of Exmouth South)
Groundwater resources
Groundwater from the karstic Cape Range limestone aquifer is the major freshwater resource in the Exmouth plan area. It is used to supply the town with drinking water and water for public amenities, domestic garden bores, tourism, defence and industrial uses.
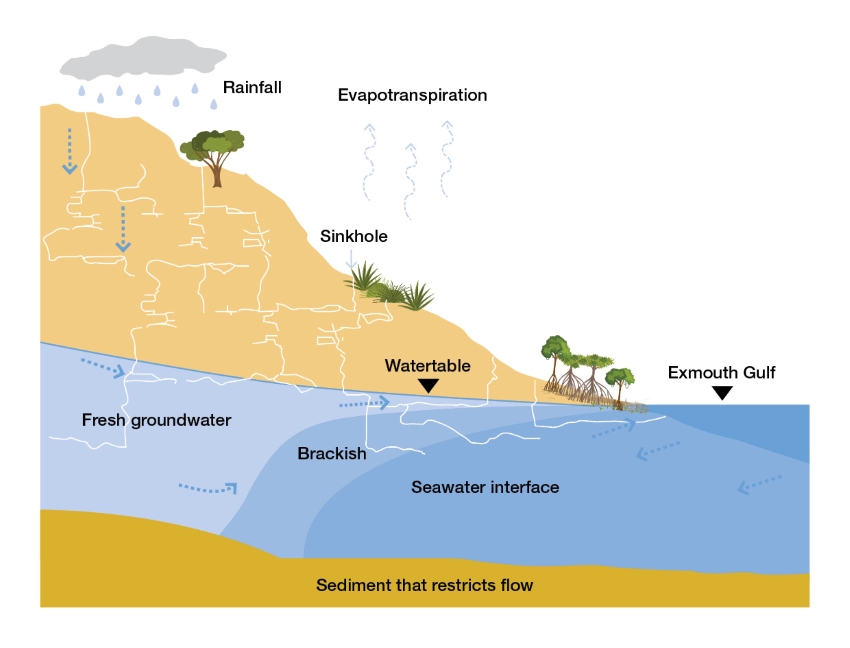
The aquifer is a lens of fresh groundwater overlying saltwater in the Cape Range limestone formation (see conceptual cross-section below). The aquifer and the Cape Range subterranean waterways support unique and important values such as a rich diversity of stygofauna and troglofauna.
The Cape Range subterranean waterways are listed in the Directory of Important Wetlands in Australia. The Cape Range Remipede Community at Bundera sinkhole and the Camerons Cave Troglobitic Community in the Exmouth townsite are threatened ecological communities recognised and protected under the Western Australian Biodiversity Conservation Act 2016.
The high diversity of subterranean species also contributes to the Ningaloo Coast World Heritage listing, meeting the UNESCO criterion x:
to contain the most important and significant natural habitats for in-situ conservation of biological diversity, including those containing threatened species of outstanding universal value from the point of view of science or conservation.
A conceptual cross-section of the Cape Range limestone groundwater system of the Exmouth Peninsula, from Cape Range east to the Exmouth Gulf
The deeper, confined Birdrong Sandstone aquifer is found at depths of about 1,000 metres and contains saline water. The Birdrong Sandstone aquifer is managed under the Carnarvon Artesian Basin water management plan.